Sampling Distribution the sampling distribution is the distribution of all possible values that can be assumed by some statistic computed from samples of the same size randomly drawn from the same population. A distribution of all possible summary statistics from a single random sample from the same population.
Lesson 4 Sampling Distributions
Not just the handful of samples collected ALL 3 different distributions Population Distribution-- gives values of a variable for ALL INDIVIDUALS in the population.
. A A normal curve for which probabilities are obtained by standardizing. It describes a range of possible. A distribution of all parameters from the population that is to be randomly sampled.
IT IS THE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF THE SAMPLE STATISTIC. Examples of statistics are the mean median mode standard deviation range. Which of the following best describes a sampling distribution of a statistic.
It is the probability that the sampling statistic equals the parameter of interest. B The mechanism that determines whether the random sampling was effective. T-test vs Z-test Uniform distribution.
Mean proportion and T-sampling distribution. It is a distribution of all the statistics calculated from all possible samples of the same size. The mechanism that determines whether the random.
--the sampling distribution is an imaginary collection of all of the values that a statistic might have taken for all possible random samples --for example dont mistakenly think that the CLT says that data are normally distributed as long as the sample is large enough. Which of the following best describes the sampling. Which best describes a sampling distribution model of a statistic.
It is the probability that the sampling statistic equals the parameter of interest. There are TWO distributions 1. The mean refers to the average value.
Using the procedures discussed in Chapter 5 Frequency Distributions the following histogram can be constructed to picture this data. A simple random of 50 adults were asked to reveal their gross annual incomes. The sampling distribution of a statistic is the distribution of values taken by the statistic in ALL POSSIBLE SAMPLES of the same size from the same population.
These numbers constitute a sample distribution. Which of the following best describes the sampling distribution of a statistic. It is a histogram of sample statistics from all possible samples of the same size.
A sampling distribution is a statistic that is arrived out through repeated sampling from a larger population. Which of the following best describes a sampling distribution of a statistic. Math world sampling distribution of the statistic which we model with a Normal model based on the Central Limit Theorem.
It may be considered as the distribution of the statistic for all possible samples from the same population of a given size. It is the distribution of all of the statistics calculated from all possible samples of the same size. In classic statistics the statisticians mostly limit their attention on.
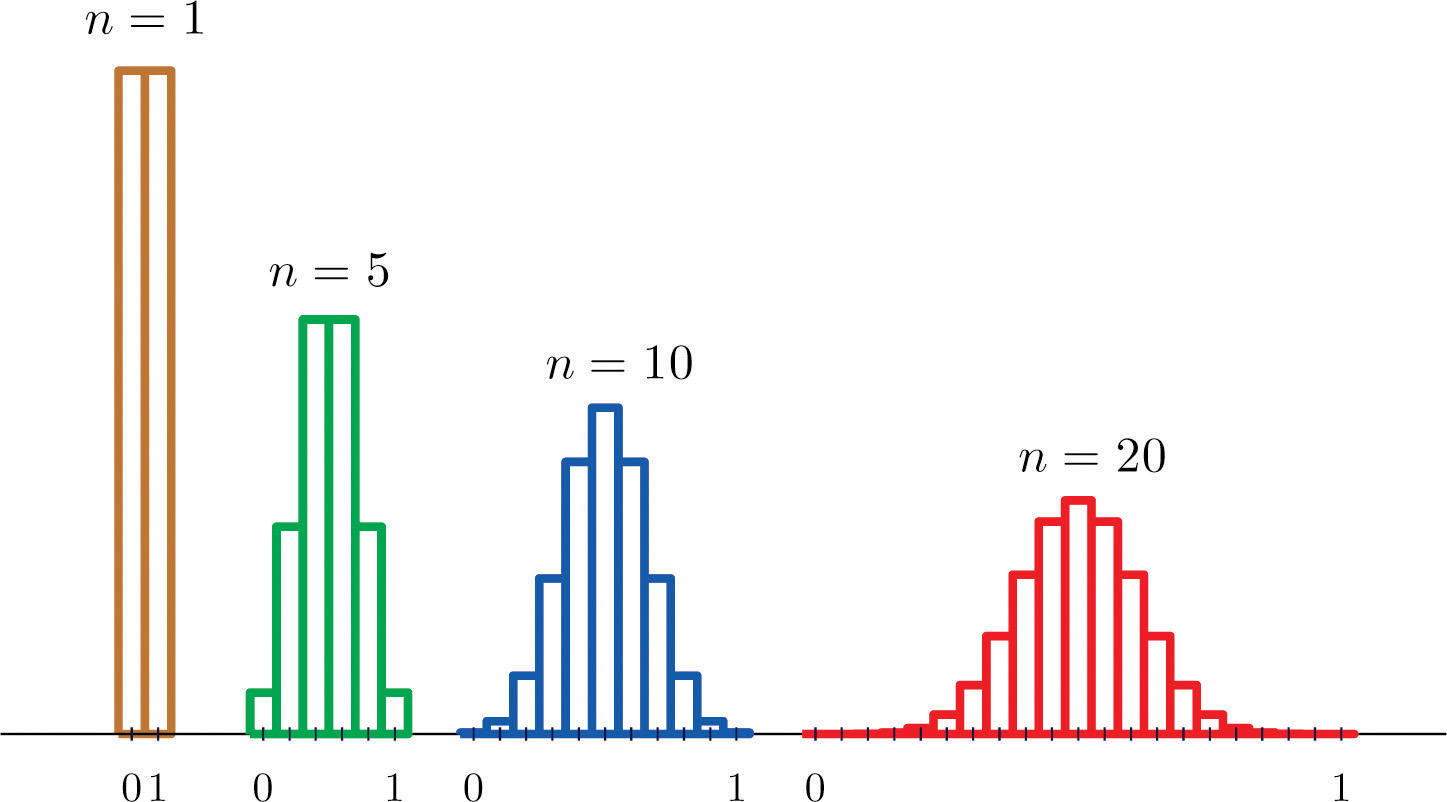
Basic truths about sampling distributions - Statistic is a random quantity -our parameter does not vary. As the sample size n increases t-distribution acts as normal distribution where the considered sample size is greater than 30. Real world distribution of the sample which we might display with a histogram.
CA distribution of a single statistic from repeated random samples of the same size from the same population. Note the -ing on the end of Sample. A sampling distribution refers to a probability distribution of a statistic that comes from choosing random samples of a given population.
It is the probability distribution of all the values that are contained in all possible samples of the same size. Sampling distribution of statistic is the main step in statistical inference. A sample distribution is a statistical concept based on repeated sampling conducted within a group or population A sampling distribution is plotted as a graph usually shaped as a bell curve based on the sample data.
Which best describes a sampling distribution model of a statistic. The sampling distribution of a statistic is the distribution of that statistic considered as a random variable when derived from a random sample of size n n. There are three types of sampling distribution.
In addition to the frequency distribution the sample distribution can be described with numbers called statistics. It is the probability distribution of all values that are contained in all possible sample of the. Sampling Distribution Is a distribution of a sample statistic in all possible samples of the same size from the same population.
It describes ALL POSSIBLE VALUES that can be assumed by the statistic. Also known as a finite-sample distribution it represents the distribution of frequencies on how spread apart various outcomes will be for a. Examples of statistics that are commonly presented in research are the sample mean and standard deviation.
These two values are often presented together. It looks and sounds similar to the Sample Distribution but in reality the concept is much closer to a population model. Answer choices It is the probability that the sample statistic equals the parameter of interest.
0 Comments